John Deere & Company has a long history of providing quality diesel engines to its customers, from its first in 1949 to today’s Tier 4 PowerTech engine. Throughout this period of time, there have been several exciting developments that have helped shape not just the evolution of diesel engines, but also John Deere history as a whole.
Access the top performing equipment on the market. Explore our inventory of John Deere machinery!
What Are the Different Types of John Deere Diesel Engines?
John Deere has come a long way since it manufactured its first diesel engine. Here are the John Deere diesel engines and their key features that are still in production today.
1996 Tier 1/Stage I Technology
In 1996, John Deere manufactured the Stage 1 Technology for its diesel engine in hopes to achieve established baseline levels for particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The John Deere Tier 1 was a diesel engine designed with a high-pressure fuel system, multiple aspirations, larger displacements, and engine calibration, with 2- or 4- valve cylinder heads. This provided customers with new engine technology that was fuel-efficient, higher peak torque, and increased power density and range.
2001 PowerTech Tier 2/Stage II Technology
Building off of the technology from the Tier 1 engine, John Deere released its PowerTech Tier 2 diesel engine in 2001. This diesel engine reduced PM by 50% and NOx by 20%, resulting in an even more fuel-efficient engine with a compact design that exceeded the Tier 1 500 horsepower with 600 horsepower. In addition, the PowerTech engine featured air-to-air cooling enhancements which made more use of after-cooling to help reduce emissions.
2006 PowerTech Tier 3/Stage III A Technology
In 2006, John Deere released the Tier 3 PowerTech diesel engine. This engine established an unparalleled record of best-in-class fuel economy and offered a higher power bulge than all other engine models. In addition, this engine featured more electronic controls which improved engine calibration and lowered fuel emissions.
2011 PowerTech Interim Tier 4/Stage III B Technology
PowerTech Interim was the next John Deere diesel engine released in 2011. Along with the new benefits of the Tier 3 diesel engine, the PowerTech Interim Tier featured 90% reduction in PM, 50% reduction in POx, ultra-low sulfur diesel, improved noise reduction, and transient response. And with these enhancements, customers saw improved high-altitude operation, greater machine productivity, and increased power density for each engine platform, so they could do the same job with a smaller displacement engine.
2014 PowerTech Final Tier 4/ Stage IV Technology
Lastly, in 2014, John Deere released the PowerTech Final Tier 4, which represents the engine with the highest level of clean air regulations proposed to date. This was a huge success for John Deere diesel engines as this model reduces 80% of nitrogen oxide emissions.
What Are the Benefits of John Deere Diesel Engines?
As mentioned above, John Deere diesel engines have seen a series of improvements since they were first manufactured. However, their diesel engines have also established some key benefits that set the John Deere diesel engine apart from the rest. These benefits include:
- Optimized emissions solution
- Fuel and fluid efficient
- Field-proven performance
- Application integration
- Fully supported service locations
Fun Facts About John Deere Diesel Engines
Now that we’ve outlined the lineage and benefits of John Deere diesel engines, let’s explore some interesting facts about diesel engines and answer some of your most important questions.
When Did John Deere First Start Making Diesel Engines?
Deere has been designing and manufacturing diesel engines since 1949.
How Much Horsepower Did the First John Deere Diesel Engine Produce?
The first Deere diesel engine, found in the Model R, produced 51 horsepower and was the first to offer a live power take-off (PTO) with its own clutch.
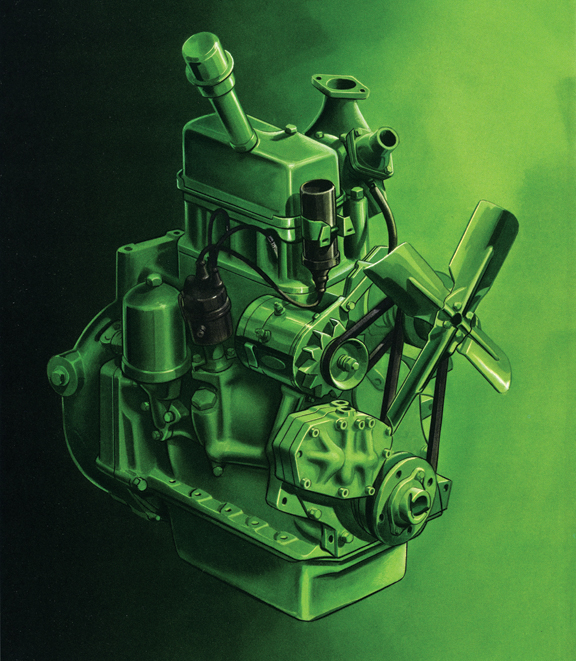
How Do the John Deere Model R Tractor Diesel Engines Work?
The innovative design of the John Deere Model R tractor featured two engines—the 416-cubic inch diesel-fired engine and a two-cylinder, gasoline-fired starter engine. The dual engines resolved certain difficulties often associated with starting diesel engines. Firstly, operators could start the engine with the pull of a lever, rather than manually turning the flywheel. Additionally, they had the capacity to warm-up the engine quickly in cold temperatures.
What Was the First John Deere Diesel-Powered Row-Crop Tractor?
In 1953, Deere launched the Model 70, the first John Deere diesel-powered row-crop tractor.
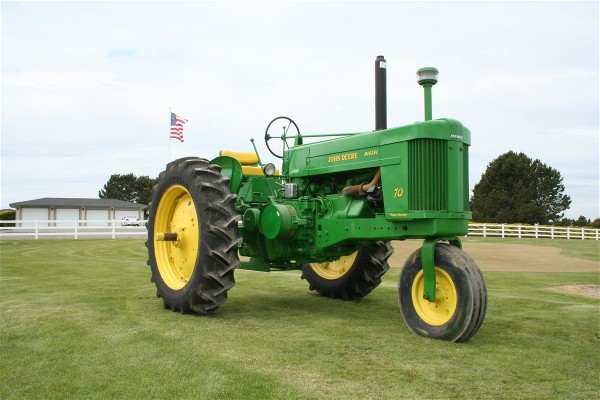

When Did John Deere Move Away From 2-Cylinder Engines?
In 1959, the model 8010 paved the way for a line of 4- or 6-cylinder diesel engines, as Deere moved away from 2-cylinder engines at the end of 1958.
When Did John Deere Produce the 300 and 400 Series Diesel Engines?
In 1960, John Deere introduced the 300 and 400 Series engines—its first-in-line 4- and 6-cylinder gasoline, LP gas, and diesel engines—in the model 1010, 2010, 3010, and 4010 tractors.
When Was the First John Deere Turbocharged Diesel Engine Released?
In 1969, Deere introduced its first turbocharged diesel engine in its 4520 row-crop tractors.
When Did John Deere Create PowerTech™ Engines?
In 1996, Deere rolled out a new breed of engines, called PowerTech™, to comply with Tier 1 standards. Since then, the company has followed a building-block approach to meeting each new regulatory Tier, systematically adopting technologies for the PowerTech platform.
What is the Horsepower of Most John Deere Diesel Engines?
John Deere diesel engines range from 49 to 600 HP.
How Many Diesel Engines has John Deere Produced?
John Deere has produced more than 5 million diesel engines.
Where to Service a John Deere Diesel Engine?
Deere diesel engines can be serviced at any of their 4,000+ service locations worldwide.
What Are John Deere Diesel Engines Used For?
John Deere diesel engines are produced for agriculture, construction, forestry, mining, generator drives, marine equipment, and thousands of other applications around the world.
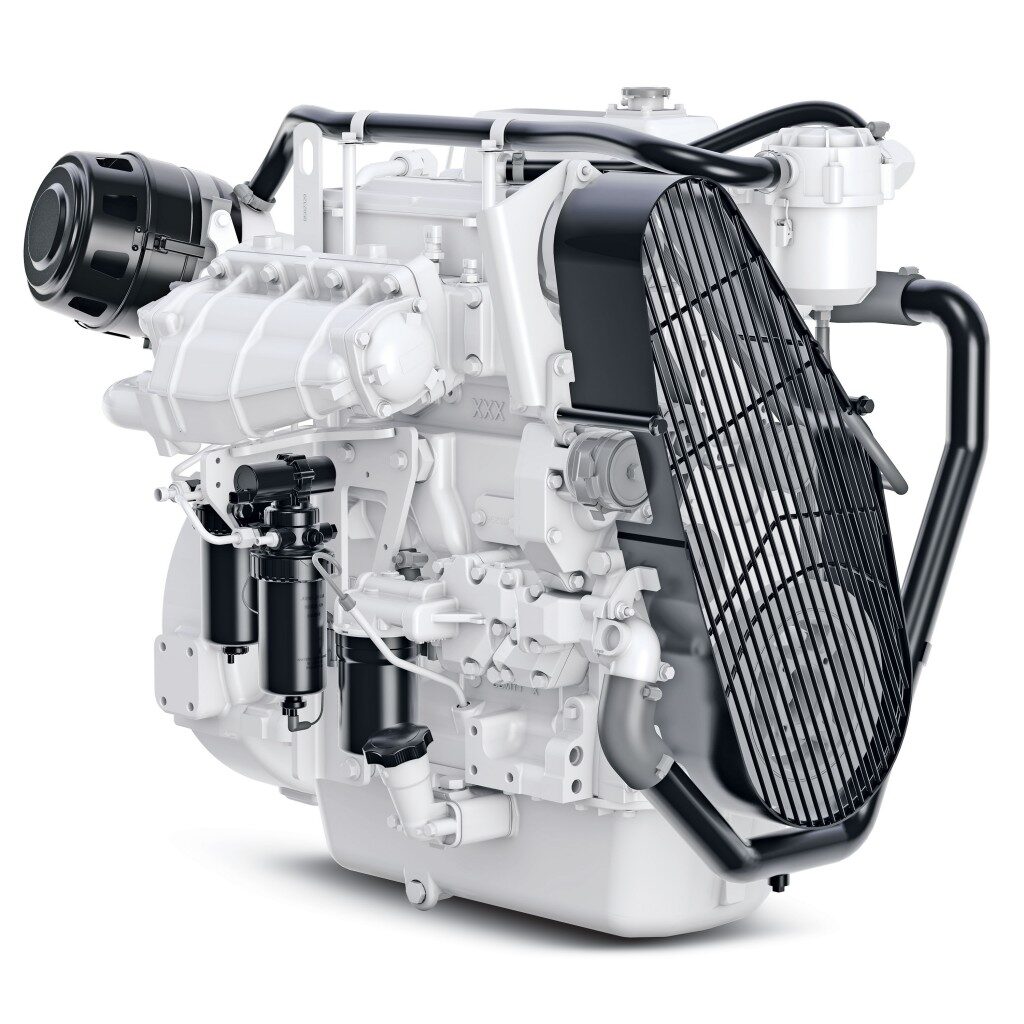

When Did John Deere Start Producing Diesel Marine Engines?
John Deere has been producing diesel marine engines for more than 30 years.
What Engine Had the Most Horsepower in the 1960s?
The 8010 produced a significant amount of power for its time – the 1960s – with 215 horsepower.
When Was the First Diesel Powered Garden Tractor Produced?
The John Deere 300 series included the company’s first diesel-powered lawn and garden tractor.

What is the Horsepower of the John Deere 9R/9RT?
Diesel engines in the John Deere 9R/9RT Series feature 560 horsepower and are among Deere’s largest pieces of equipment.
Where Are John Deere Engines Manufactured?
John Deere engines are produced in different factories worldwide: Saran (France), Waterloo (USA), Torreon (Mexico), Pune (India), and Rosario (Argentina).
What Can a John Deere Engines be Used For?
John Deere engines are distributed to more than 700 OEMs worldwide for use in construction, marine, agricultural, and forestry machines, as well as air compressors, generator sets, irrigation pumps, and natural gas on-highway applications.
What Makes John Deere Diesel Engines Unique?
Diesel engines designed and manufactured by John Deere aim to provide excellent torque, fuel efficiency, and durability.
What Manufacturer was the First to Certify Diesel Engines?
John Deere was one of the first engine manufacturers to certify 75-to-174-hp diesel engines as compliant with EPA Interim Tier 4, EU Stage III B, and CARB emissions regulations.

Learn More About John Deere Diesel Engines
John Deere diesel engines have been instrumental in the manufacturing of thousands of products and applications around the world. The company has set high standards for providing customers with quality engines, as its impressive history demonstrates.
If you have any questions about the John Deere engines or other types of machinery, you can contact your local John Deere dealer or watch the video below.
If you enjoyed this post or want to read others, feel free to connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, or Instagram!