This was originally posted on the John Deere, Straightforward Blog this past January. You can view the original post here.
As conversations around emissions regulations continue, it’s important to be able to “talk the talk.” Following is our glossary of terms commonly used when speaking about emissions, broken down in your language to help you better understand the new IT4 requirements and their impact.
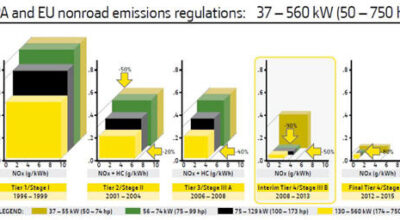
Interim Tier 4 (IT4) – fourth stage in the emissions regulation for new, non-road diesel engines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for North America. This reduces particulate matter by 90 percent along with a 50 percent drop in NOx compared to Tier 3.
Final Tier 4 – final stage in the emissions regulations for new, non-road diesel engines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for North America that take effect in as early as 2014. Final Tier 4 requires further reduction of PM by 80 percent.
Particulate Matter (PM) – also known as “soot” or “smoke” is a non-gaseous product of combustion. It is essentially an incomplete combustion of diesel fuel.
Nitrogen Oxide – or NOx, contributes to the formation of atmospheric pollution. It interacts with other chemicals and sunlight to form ground-level ozone, commonly referred to as “smog.”
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) – an alternate emissions control strategy to reduce NOx when combined with a diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). The SCR system lowers NOx while the DOC reduces PM.
Cooled EGR – As its name implies, cooled EGR cools and mixes measured amounts of exhaust gas with incoming fresh air to lower the engine amp;rsquo;s peak combustion temperature, thereby reducing NOxto an acceptable level. Exhaust gases are routed through an exhaust filter, consisting of a DOC and diesel particulate filter (DPF). Particulate matter is trapped in the filter and—through a process called passive regeneration, which utilizes normal engine exhaust temperatures—the PM is oxidized into nitrogen gas and carbon dioxide, then expelled through the exhaust pipe. Cooled EGR paired with an exhaust filter requires less operator involvement and is a simpler, proven, fuel-efficient, and less-costly technology compared to alternative solutions. This is what our customers told us they want.
Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) – The DOC is part of the exhaust filter that reduces carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and some PM.
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) – The DPF traps and holds particulates remaining in the exhaust stream. Trapped particulates are eventually oxidized within the DPF through regeneration.